
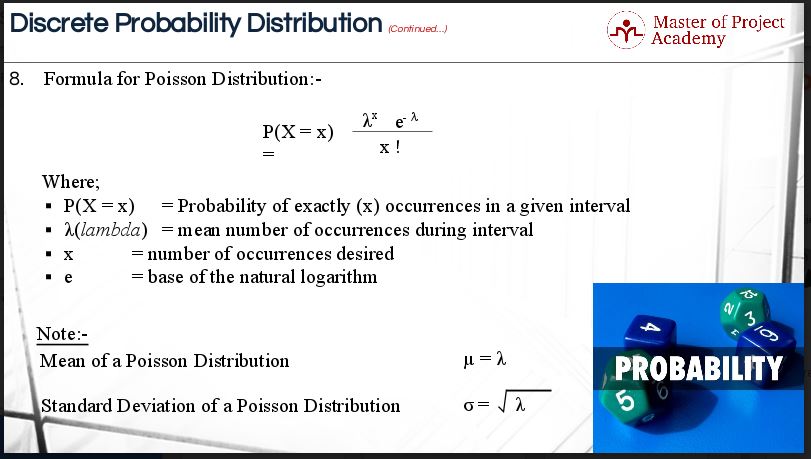
Poisson relations thermodynamics calculator how to#
How to calculate the efficiency of a heat engine?.What is the operation principle of heat engines?.What are some equivalent formulations of the Second Law of Thermodynamics?.What does the Second Law of Thermodynamics say?.What happens to the entropy in the universe during a thermal process?.
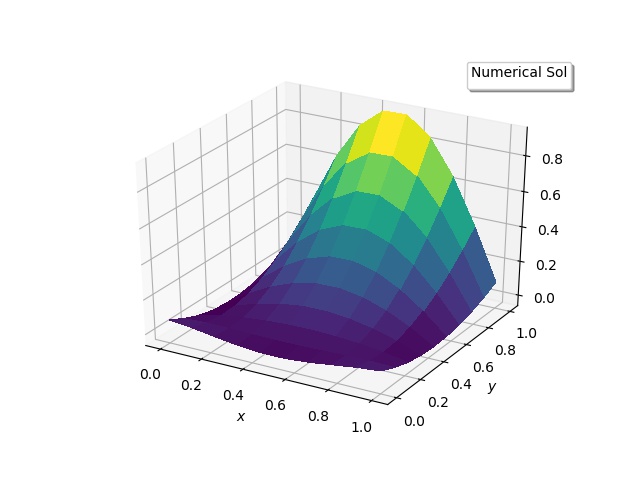
What are the factors affecting the entropy of a thermodynamic system?.What are reversible and irreversible processes?.Why the first law of thermodynamics is not sufficient in explaining all thermal-related phenomena?.In this Physics tutorial, you will learn: you can access all the lessons from this tutorial below. The tutorial starts with an introduction to Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics and is then followed with a list of the separate lessons, the tutorial is designed to be read in order but you can skip to a specific lesson or return to recover a specific physics lesson as required to build your physics knowledge of Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Let's put substitute values in the equation of C m.There are 6 lessons in this physics tutorial covering Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics. $$where,\ C = heat\ capacity\ and\ n = moles$$ It is an intensive property, ie it does not depend on amount of matter present in the substance.It is defined as heat capacity per unit mole.Molar heat capacity is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 mole of a substance by 1 K.$$where,\ C = Heat\ capacity\ and\ m = mass\ in\ gram$$ It is an intensive property because it does not depend on amount of matter present in the substance (it is expressed as per unit gram of mass).It can also be defined as the heat capacity per unit gram of mass.Specific heat capacity is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 K.$$where,\ q = heat\ and\ T = temperature$$ It is denoted by C and is an extensive property, ie, it depends on the amount of matter present in the substance.We can define heat capacity as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a given mass of substance by 1 Kelvin (or 1 ℃).Thermodynamics | Heat Capacity Heat Capacity:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
